Exciplex-enabled high-efficiency, fully stretchable OLEDs
TL;DR
Researchers developed fully stretchable OLEDs with record efficiency using an exciplex-assisted phosphorescent layer and MXene-contact electrodes, achieving 17.0% EQE and minimal luminescence loss under strain.
Key Takeaways
- •Incorporated an intrinsically stretchable exciplex-assisted phosphorescent layer to achieve over 200% stretchability and 21.7% EQE.
- •Integrated MXene-contact stretchable electrodes with high mechanical robustness and tunable work function for efficient charge injection.
- •Enabled fully stretchable OLEDs with a record 17.0% EQE and minimal performance loss under 60% strain.
Tags
Abstract
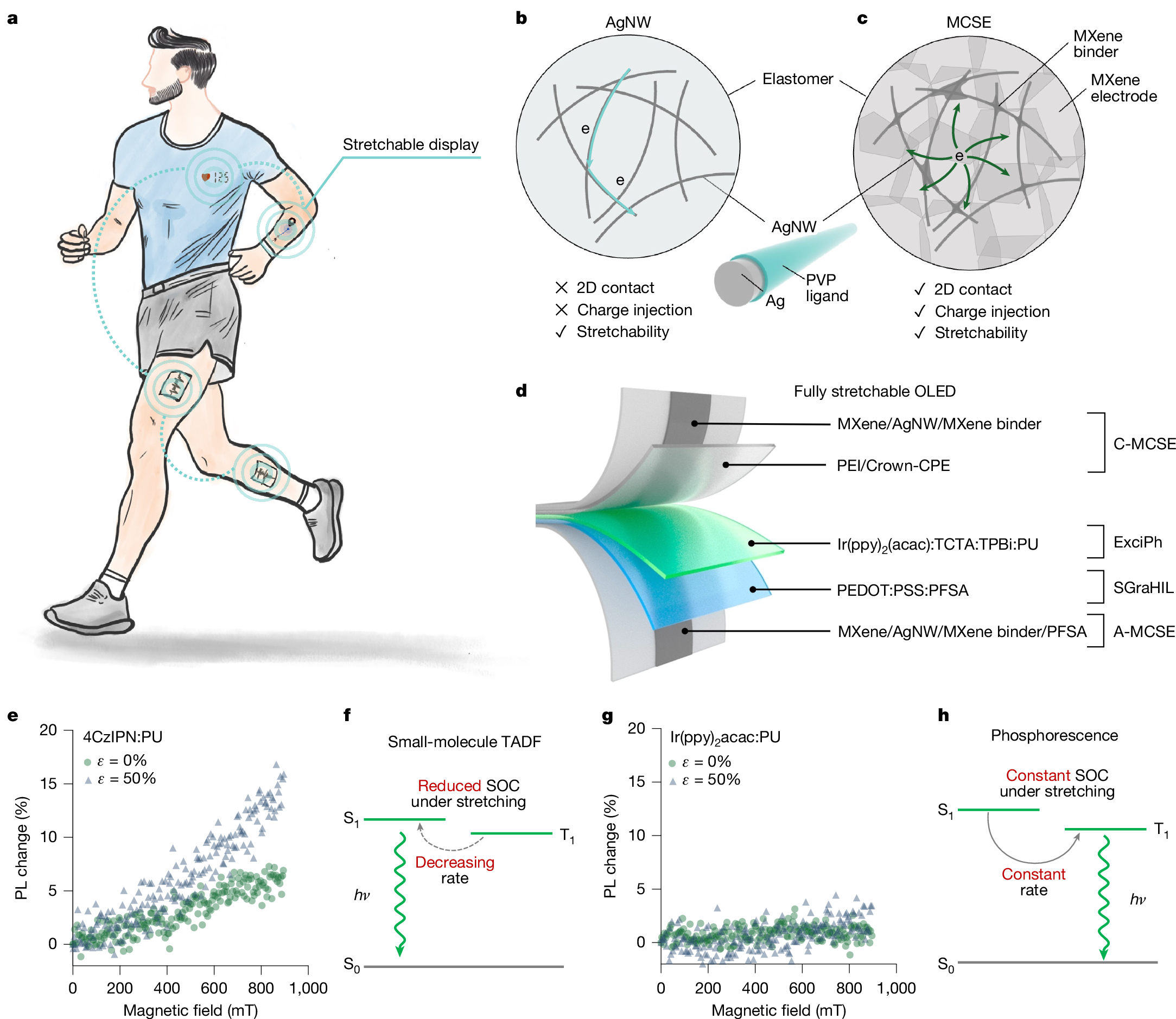
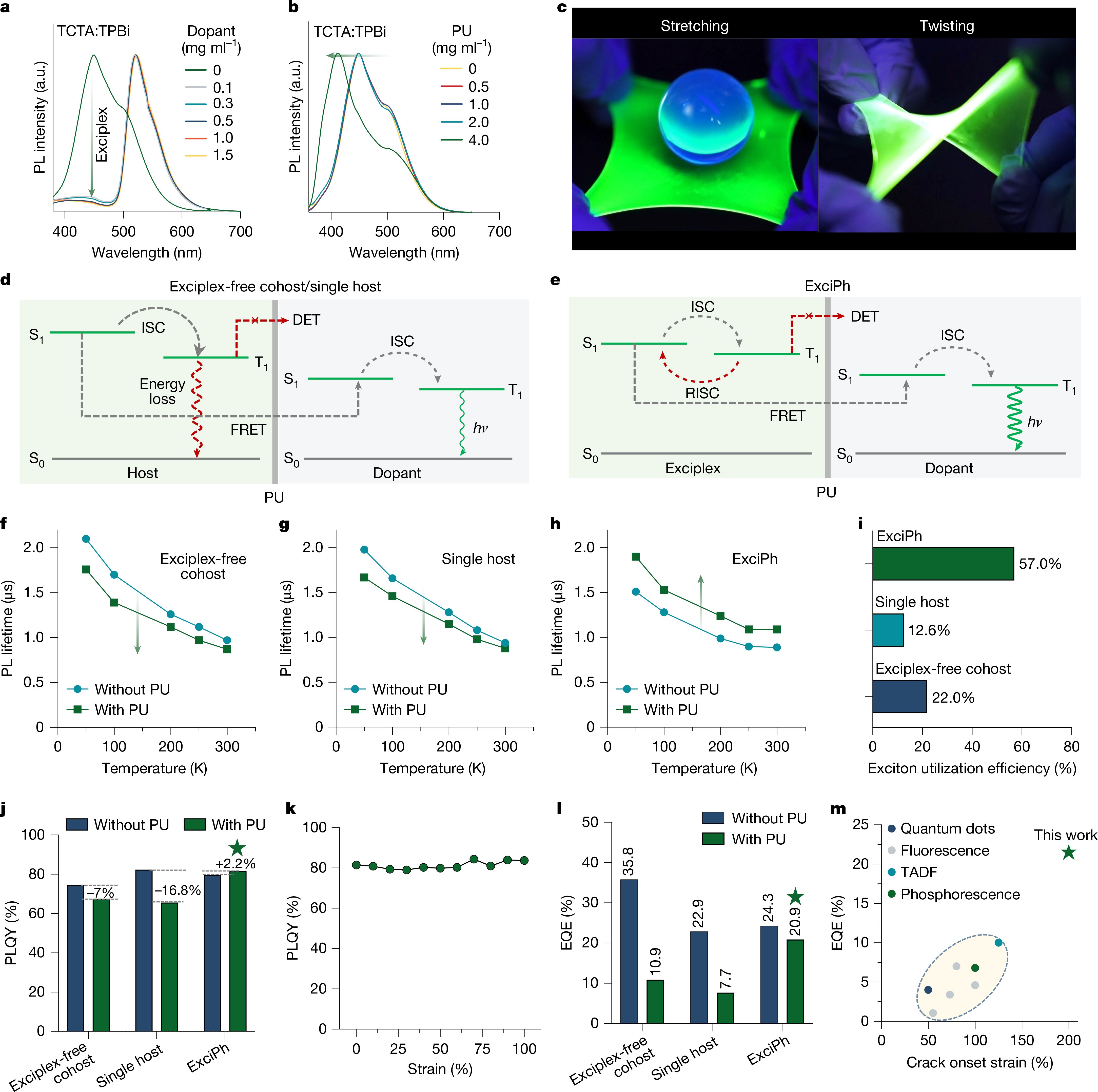
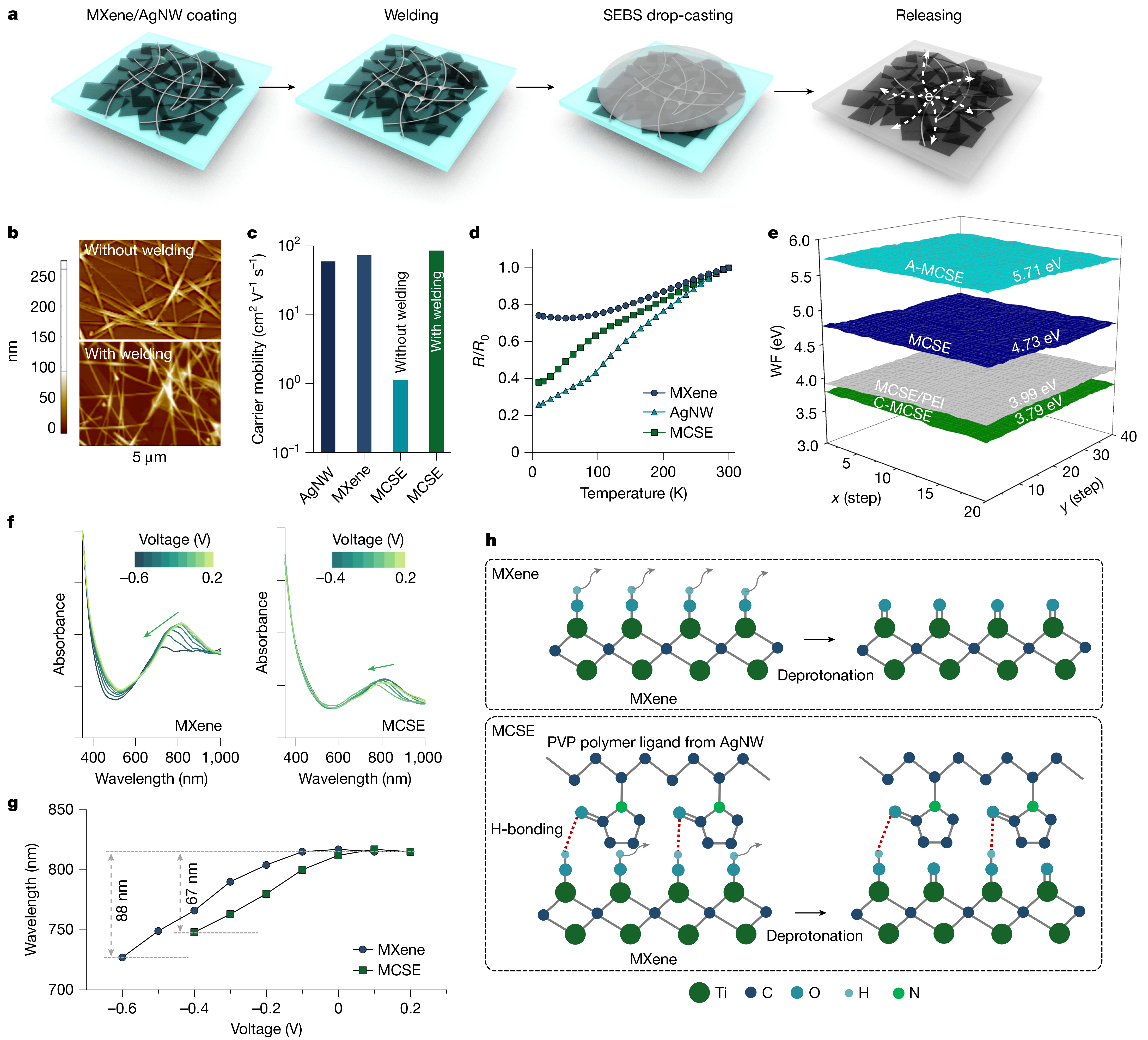
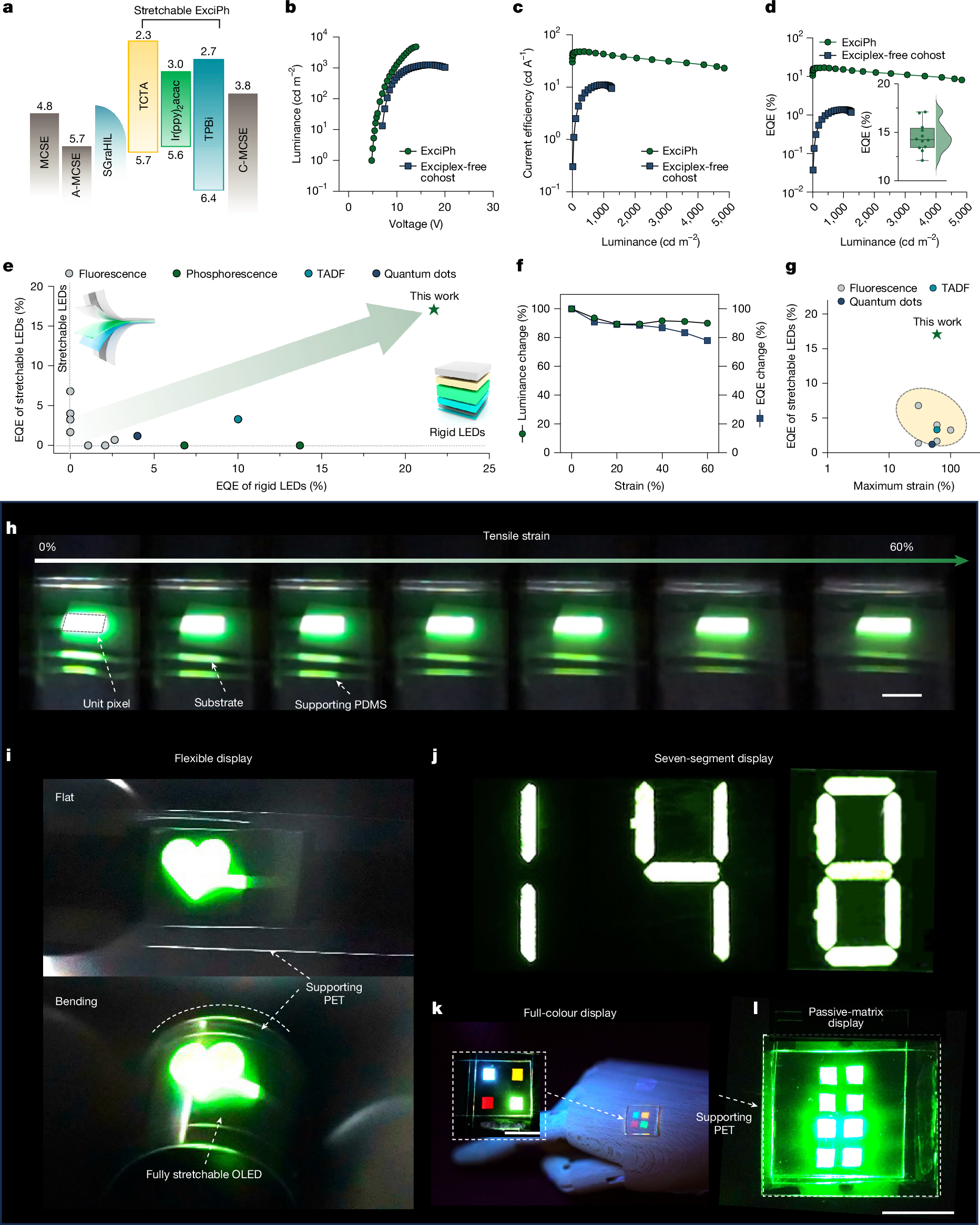
Fully stretchable organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), composed entirely of intrinsically stretchable materials, are essential for on-skin displays1,2,3. However, their low device efficiency has been a persistent barrier to practical applications for more than a decade4. Here we addressed this challenge by incorporating an intrinsically stretchable exciplex-assisted phosphorescent (ExciPh) layer. The elastomer-tolerant triplet-recycling mechanism mitigates exciton energy transfer limitations arising from the insulating elastomer matrix, yielding a light-emitting layer with more than 200% stretchability and an external quantum efficiency (EQE) of 21.7%. To translate this performance to fully stretchable devices, we integrated MXene-contact stretchable electrodes (MCSEs), which feature high mechanical robustness and tunable work function (WF), ensuring efficient hole and electron injection. These advances enable fully stretchable OLEDs with a record EQE of 17.0% and minimal luminescence loss under 60% strain. This approach to designing high-efficiency, mechanically compliant optoelectronics will enable the next-generation wearable and deformable displays.
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Data availability
All of the data supporting this manuscript are available in the form of Source Data files and the supplementary material. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Zhang, Z. et al. High-brightness all-polymer stretchable LED with charge-trapping dilution. Nature 603, 624–630 (2022).
Liang, J., Li, L., Niu, X., Yu, Z. & Pei, Q. Elastomeric polymer light-emitting devices and displays. Nat. Photon. 7, 817–824 (2013).
Matsuhisa, N. et al. High-frequency and intrinsically stretchable polymer diodes. Nature 600, 246–252 (2021).
Zhou, H., Kim, H.-W., Jeong, W. J. & Lee, T.-W. Toward intrinsically stretchable OLEDs with high efficiency. Adv. Mater. 37, 2420008 (2025).
Shi, X. et al. Large-area display textiles integrated with functional systems. Nature 591, 240–245 (2021).
Kim, J.-H. & Park, J.-W. Intrinsically stretchable organic light-emitting diodes. Sci. Adv. 7, eabd9715 (2021).
Zhou, H., Kim, K.-N., Sung, M.-J., Han, S. J. & Lee, T.-W. Intrinsically stretchable low-dimensional conductors for wearable organic light-emitting diodes. Device 1, 100060 (2023).
Adachi, C., Baldo, M. A., Thompson, M. E. & Forrest, S. R. Nearly 100% internal phosphorescence efficiency in an organic light-emitting device. J. Appl. Phys. 90, 5048–5051 (2001).